▶ Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Schema Markup
- Importance of Schema Markup for Travel‑Specific Pages
- How to Implement Schema Markup for Itineraries
- How to Implement Schema Markup for Offers
- How to Implement Schema Markup for Events
- Measuring the Impact of Schema Markup on Visibility
- Best Practices and Common Mistakes
- Conclusion
Introduction
In today’s highly competitive travel market, simply publishing destination guides, tour offers and event listings isn’t enough. To stand out in search engines and capture high‑intent travellers, agencies must help search engines understand the nature of their pages.
That’s where schema markup (structured data) comes in. According to one study, travel websites that properly implement schema saw up to 30‑35 % higher organic click‑through rate (CTR).
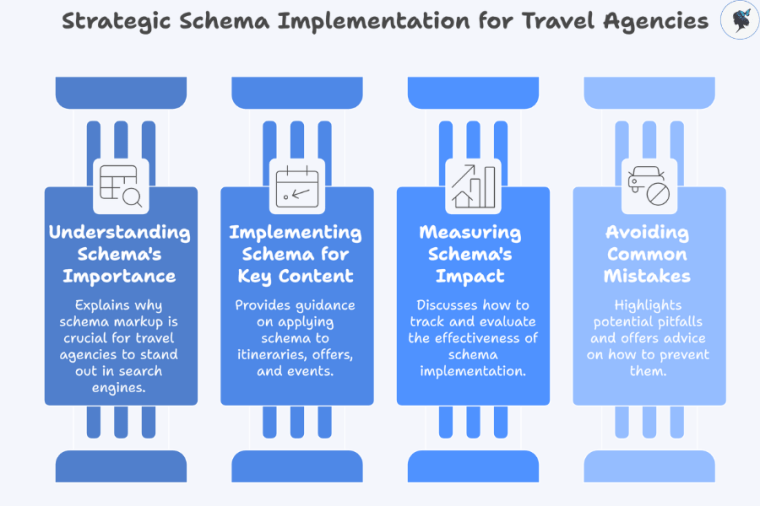
For travel agencies, pages like itineraries, limited‑time offers, and seasonal events are prime candidates for schema markup—but they also present unique challenges (changing dates, availability, etc.). This article will help you understand why schema matters, how to implement it for key travel content types (itineraries, offers, events), how to measure its impact, and ensure you avoid common mistakes.
Wander Women Hot Tip: Start by auditing your key pages—identify your top itineraries, offers and event pages—and check whether they currently include schema. Use that baseline for measurement.
Understanding Schema Markup
Schema markup (also called structured data) is code you add to your webpages (usually in JSON‑LD format) that describes the content’s meaning in a way search engines understand.
Search engines like Google use this to display enhanced listings known as rich results: these might show star ratings, prices, dates, or even event information directly in SERPs. For instance, Google’s documentation for the Event type shows that event‑marked pages can feature in Google’s event‑search experience.
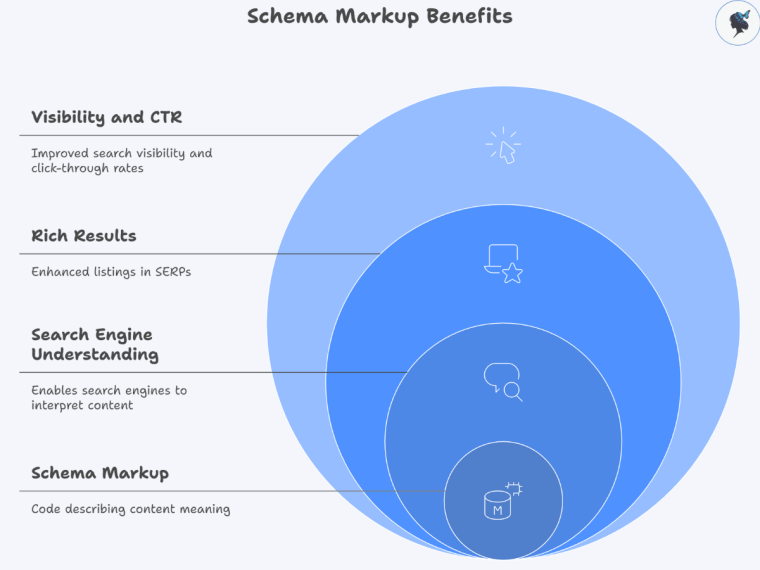
While schema isn’t a direct ranking factor, its impact on visibility and click‑through rates is substantial. For example, one article noted that pages with rich results can enjoy 58 % CTR compared to 41 % for standard listings.
Wander Women Hot Tip: Use Google’s Rich Results Test or Structured Data Testing Tool to validate your markup before publishing. Avoid implementing schema without testing.
Importance of Schema Markup for Travel‑Specific Pages
Why travel pages especially benefit:
- Itineraries: Complex multi‑day plans, multiple destinations, and activities – schema helps search engines interpret structure.
- Offers: Limited time, price, availability – markup helps highlight pricing directly in search.
- Events: Dates, tickets, location – schema helps appear in event carousels.
For travel websites, comprehensive schema implementation led to observation of a 35 % higher CTR compared with competitors lacking structured data.
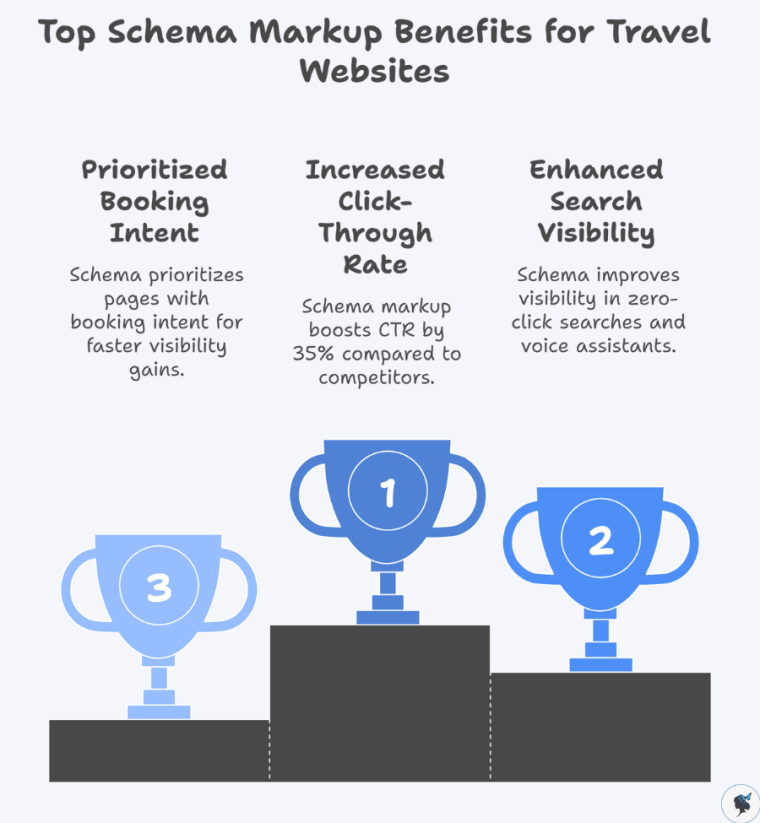
Moreover, given the rise of “zero‑click searches”, voice assistants and AI‑driven search experiences favour content that is richly structured and clearly defined. For travel agencies, this means schema isn’t optional—it’s increasingly fundamental.
Wander Women Hot Tip: Prioritise pages with booking intent (offers) and planning intent (itineraries/events). These are the pages where schema delivers the fastest visibility gains.
How to Implement Schema Markup for Itineraries
Step‑by‑step guide:
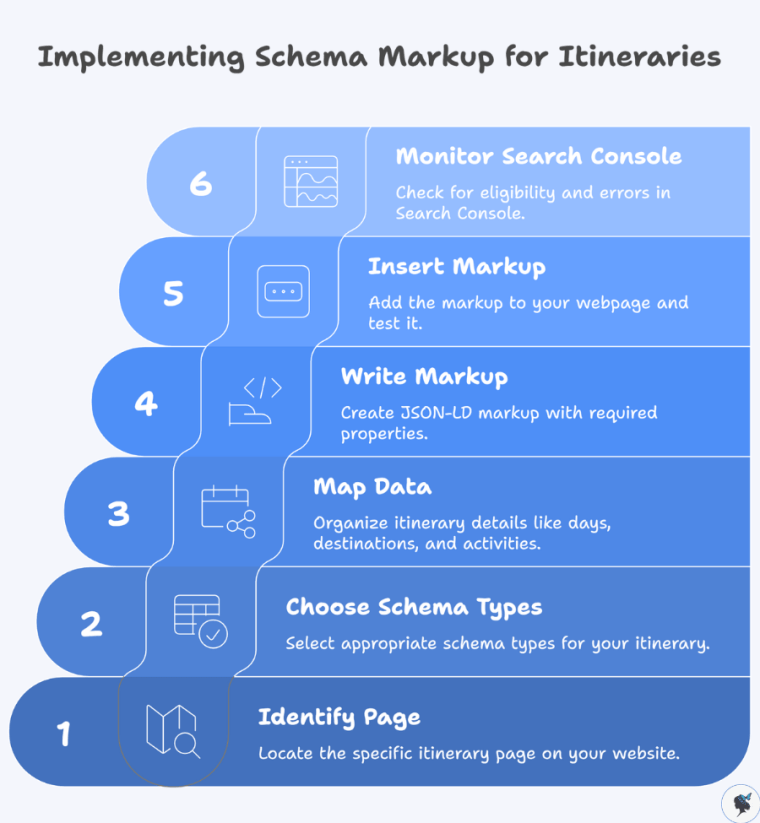
- Identify the itinerary page: e.g., “7‑day Italy Highlights Tour”.
- Choose relevant schema types:
Itinerary,TouristTrip,Place,TouristAttraction. - Map your data: days, destinations, activities, durations, images.
- Write the JSON‑LD markup, ensuring required properties.
- Insert the markup (ideally in
<head>or just before</body>) and run the Rich Results Test. - Monitor Search Console. Look in the Enhancements section for eligibility and errors.
Wander Women Hot Tip: For multi‑day tours, break out each day as an item in the itinerary array—not only does this help search engines, but it can also support more structured snippets.
You might like: Tips for Writing Travel Itineraries That Sell.
How to Implement Schema Markup for Offers
Why it matters:
Offers often involve price, validity, availability and limited‑time deals—all data search engines love for enhanced listings.
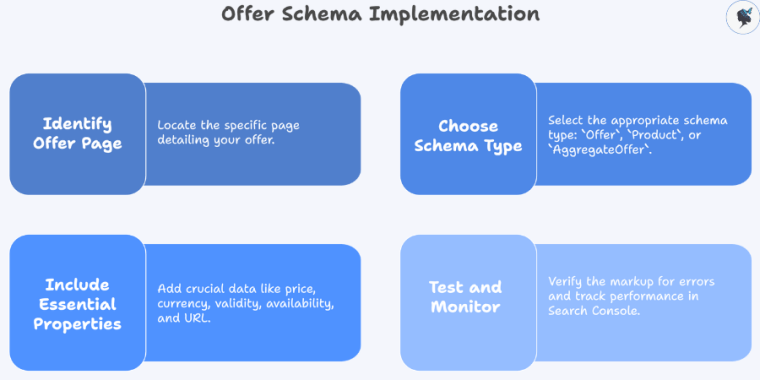
Implementation steps:
- Identify your offer page: e.g., “Summer 2026 Beach Special – 10 % off”.
- Use
Offer,Product, orAggregateOfferschema. - Include essential properties:
price,priceCurrency,validFrom,validThrough,availability,url. - Test and fix errors, then monitor impressions and CTR in Search Console.
Wander Women Hot Tip: Remember to update your valid dates, availability and price each season. Stale markup can mislead search engines and users, reducing effectiveness.
More about managing seasonal content here.
How to Implement Schema Markup for Events
Why events deserve schema:
Events like festivals, guided tours or seasonal happenings have a date/time/location format that search engines replicate in event carousels. Google’s own documentation confirms event markup can boost discoverability.
Implementation steps:
- Identify event pages (e.g., “Venice Carnival 2026”).
- Use
Event(orTouristEvent). - Required properties:
name,startDate,endDate,location,image,offers. - Test and monitor in Search Console.
Wander Women Hot Tip: For recurring events, update your event page annually—and archive past editions—so markup remains current and avoids “expired event” signals to search engines.
Measuring the Impact of Schema Markup on Visibility
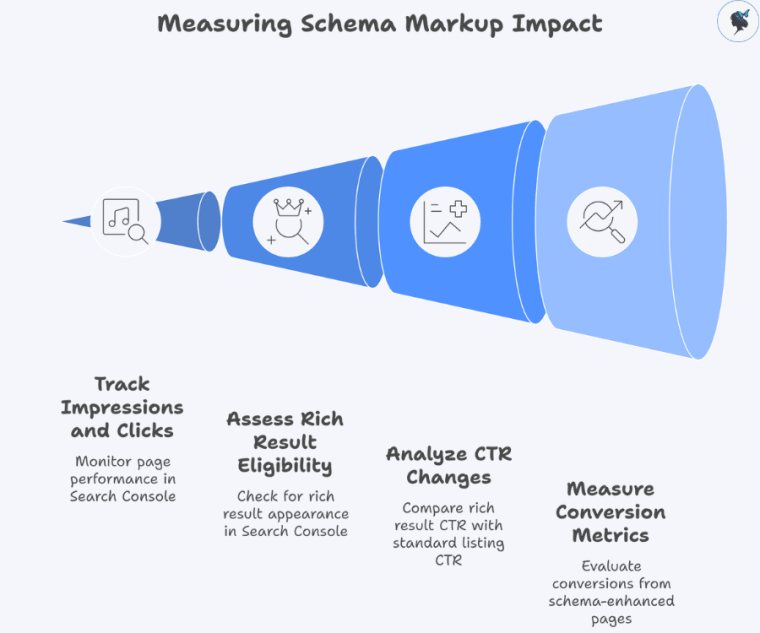
What to measure:
- Impressions and clicks for pages with schema (via Search Console: Performance).
- Rich result eligibility and appearance (Search Console: Enhancements).
- CTR changes pre‑ and post‑implementation (rich result vs standard listing).
- Conversion metrics (bookings/inquiries) from schema‑enhanced pages vs baseline.
Tools you’ll use:
- Google Search Console
- Google Analytics (traffic, user behaviour, conversion)
- Ahrefs/Semrush (SERP visibility, rich snippet tracking)
Wander Women Hot Tip: Set up a before/after report: pick 3 high‑priority pages, implement schema, then track metrics for 90 days to measure lift in visibility, click‑through and conversions.
Best Practices and Common Mistakes
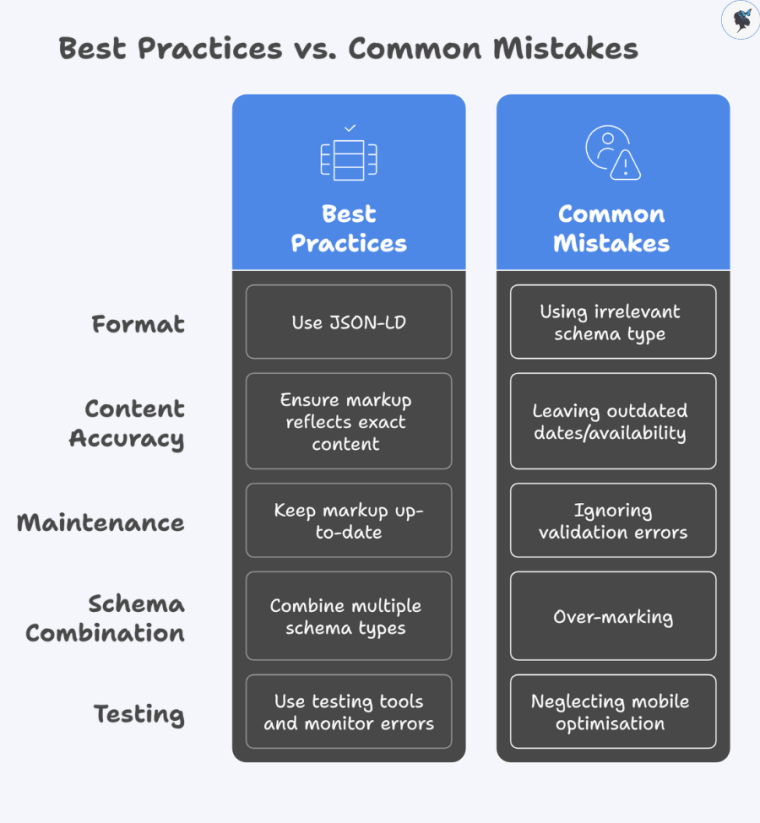
Best Practices:
- Use JSON‑LD format (Google’s recommended format).
- Ensure markup reflects exact on‑page content (primary element rule).
- Keep markup up‑to‑date with changing offers, events and itineraries.
- Combine multiple schema types when relevant (e.g.,
Offer+TouristTripon one page). - Use testing tools and monitor errors regularly.
Common Mistakes:
- Using irrelevant schema type or mismatching the page content (e.g.,
Producton an event page). - Leaving outdated dates/availability in markup, leading to stale rich features.
- Ignoring validation errors—unresolved warnings may prevent rich results.
- Over‑marking (adding schema where it doesn’t apply) which can confuse engines.
- Neglecting mobile optimisation of pages with schema—most users search on mobile and mobile SERPs are increasingly crucial.
Wander Women Hot Tip: Create a schema maintenance calendar. Review your markup every 3–6 months—or sooner for seasonal pages—to ensure continued accuracy and effectiveness.
Conclusion
Schema markup is no longer a nice‑to‑have—it’s a strategic necessity for travel agencies aiming to boost visibility, click‑throughs and bookings. By implementing tailored markup for itineraries, offers and events, and tracking the performance thoughtfully, you can gain a meaningful competitive edge in search results.
Start small: pick one key itinerary, one offer and one event page. Implement appropriate schema, validate it, and monitor the impact over 90 days. Then scale your approach across more pages.
Wander Women Hot Tip: Remember—schema is only part of the picture. Combine your structured data efforts with optimized content, speedy mobile performance and effective internal linking to maximise impact.
Need help? Contact us today!
Discover more from Wander Women Strategies
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

